As a dog owner, you might have found yourself wondering about the anatomy of your furry friend. More specifically, you may be curious about where your dog’s abdomen is located. Understanding your dog’s anatomy can help you identify any possible health issues and ensure you’re providing your pet with the best care possible. In this article, we’ll explore the location and importance of a dog’s abdomen.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding a Dog’s Anatomy
- The Abdominal Region
- Importance of the Dog’s Abdomen
- Potential Abdominal Health Issues in Dogs
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways:
- A dog’s abdomen is located between their ribcage and hind legs.
- The abdomen houses several vital organs, including the stomach, liver, and intestines.
- Regularly monitoring your dog’s abdomen can help detect potential health issues.
- Always contact a veterinarian if you suspect your dog has an abdominal issue.
Understanding a Dog’s Anatomy
When it comes to understanding your dog’s anatomy, it’s important to note that a dog’s body is divided into several regions. Each region contains specific organs and plays a vital role in your dog’s overall health. A dog’s abdomen, for instance, holds crucial organs for digestion and waste elimination.
The Abdominal Region
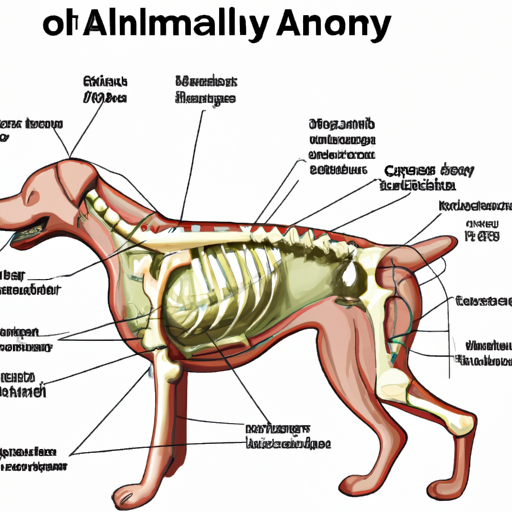
If you were to look at your dog from the side, you would notice that their body is divided into two main visible sections: the thorax (chest) and the abdomen. The dog’s abdomen is the area located between the end of the ribcage and the hind legs.
This lower section of your dog’s body houses several essential organs, including the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, kidneys, intestines, and bladder. Each of these organs plays a crucial role in your pet’s health, making the abdomen a vital part of your dog’s anatomy.
This detailed canine anatomy diagram can help you visualize where the abdomen is located in relation to other body parts.
Importance of the Dog’s Abdomen
Your dog’s abdomen is more than just a part of their body; it’s a hub of vital organs that keep them healthy and active. The stomach and intestines, for example, are responsible for digesting food and absorbing nutrients. The liver and kidneys filter out toxins from your pet’s body, and the bladder stores urine until it can be excreted.
Monitoring your dog’s abdomen can give you insight into their health. For instance, a distended or bloated abdomen can indicate issues such as gastric dilation-volvulus (GDV), also known as bloat, a life-threatening condition.
Learn more about common abdominal health issues in dogs here.
Potential Abdominal Health Issues in Dogs
There are several potential health issues that can affect a dog’s abdomen. These include:
- Gastric Dilation-Volvulus (GDV) or Bloat
- Intestinal Blockage
- Kidney Disease
- Liver Disease
- Abdominal Tumors
If you notice any changes in your dog’s abdomen, such as swelling, tenderness, or behavioral changes like loss of appetite, it’s important to consult a veterinarian.
For more dog health-related information, check out these articles on vet visits, dog nutrition, and common health issues from onetopdog.com.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is my dog’s abdomen swollen?
A: Swelling in the abdomen could be a sign of various issues, like bloat, obesity, or an internal issue. Always consult a vet if you notice changes in your dog’s abdomen.
Q: How can I tell if my dog has abdominal pain?
A: Signs of abdominal pain can include restlessness, loss of appetite, whimpering, or changes in posture. If your dog shows signs of distress, consult a vet immediately.
Q: What can cause an enlarged abdomen in dogs?
A: Several issues can cause an enlarged abdomen, including obesity, bloating, liver disease, heart failure, or tumors. It’s important to consult a vet if you notice any changes in your dog’s abdomen.
Understanding your dog’s anatomy, particularly the abdomen, can help you provide them with the best care possible. Remember, always consult a veterinarian if you notice any changes in your dog’s health or behavior. Your dog’s health and well-being rely on your vigilant care and attention.